
June 28, 2024 - by Synoptek
124 million Healthcare Records Breached in 365 Days in 2023! This February, just one ransomware attack on a company called Change Healthcare compromised about 85 million patient records, and recovery is still in progress. Due to this single attack, patients continue to face delays in testing and critical medical procedures as healthcare operations are disrupted.
The HIPAA Journal reported that healthcare data breaches alone accounted for 93.5% of all breached records in the last year.
Healthcare data breaches averaged $10.93 million in costs, significantly higher than the second-in-line financial industry’s average of $5.9 million. The severity of these breaches underscores the need for robust healthcare cybersecurity measures.
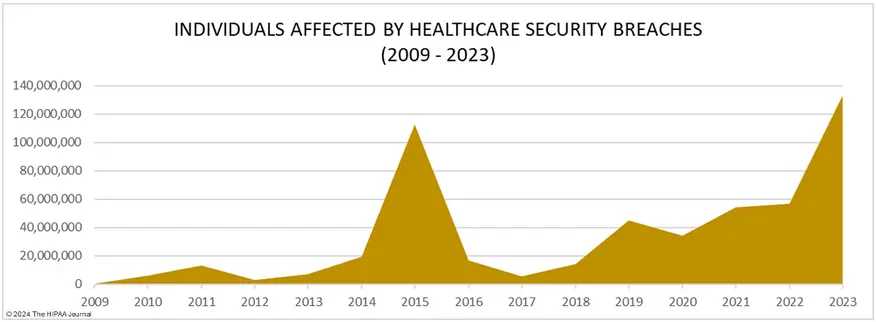
Source: The HIPAA Journal
The healthcare industry faces significant challenges in addressing sophisticated cyberattacks, often due to exploiting previously known vulnerabilities. Many healthcare organizations struggle to implement basic security measures and adhere to cybersecurity best practices due to budget constraints, talent shortages, and poor knowledge about effective resilience strategies.
Here are the key impacts and challenges that highlight the urgency of this issue:
The healthcare industry faces various cybersecurity threats that can compromise patient care, data security, and organizational operations. Healthcare organizations operate with thin margins, making investing in cybersecurity measures and recovering from financial impacts complex. Also, healthcare has an apparent shortage of cybersecurity skills, making resolving vulnerabilities efficiently and defending critical systems challenging.
Most organizations also lack a well-documented cybersecurity policy, which can easily lead to delayed or fragmented cyber-attack responses.

Here are some of the critical threats or cyber-security challenges that healthcare organizations must address:
To address these threats, healthcare organizations must adopt a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes risk assessments, implementation of security frameworks, staff training, and continuous monitoring and improvement of security measures.
Organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to building resilience to address increasing threats and challenges in the healthcare industry ecosystem. Here are key strategies to consider:
Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to your organization. Define your risk appetite, which will guide your cybersecurity strategy and investments.
Adopt industry-recognized cybersecurity frameworks such as NIST CSF, ISO 27001, or HIPAA Security Rule to establish a baseline for your security measures. Implement best practices like access controls, encryption, and regular software updates.
Stay informed about emerging healthcare sector cyber threats, such as ransomware, data breaches, and DDoS attacks, and understand their potential impact on patient care and data security.
Implement robust security controls to protect your systems and patient data, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection. Develop and regularly test incident response plans to ensure your organization is prepared to respond effectively to cyber incidents.
Educate and train employees at all levels about cybersecurity best practices, common attack vectors, and their role in protecting the organization. Build a culture of cybersecurity awareness and accountability.
Invest in advanced cybersecurity tools and technologies tailored to the healthcare industry, such as medical device security solutions, cloud security platforms, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Partner with cybersecurity experts and service providers to access specialized knowledge, resources, and support in addressing complex security challenges. Engage with industry peers, government agencies, and information-sharing and analysis organizations (ISAOs) to share threat intelligence and best practices.
Establish a robust real-time monitoring system to detect and respond to potential threats. Regularly review and enhance cybersecurity protocols based on emerging threats, industry trends, and lessons learned from incidents.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare organizations can build a strong foundation for cybersecurity resilience, protect patient care and data, and maintain trust with patients and stakeholders. However, it’s important to note that cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation to the evolving threat landscape.
Protecting data is crucial to humanizing healthcare. Cyberattacks can harm healthcare organizations in multiple ways: financially through ransom demands, reputational damage from compromised data, and disruption to critical healthcare services.
By combining industry knowledge with proactive threat intelligence, our cybersecurity experts enable healthcare players to stay ahead of threats and make healthcare more secure for everyone.
