
April 11, 2024 - by Synoptek
Patient data is the backbone of healthcare – be it sensitive personal, financial, medical, or research data. Taking care of people nowadays also translates into taking care of their data. Preserving this data is paramount to humanizing healthcare. However, frequent cyberattacks pose multifaceted threats to healthcare organizations: financial repercussions from ransom demands, reputational harm from data breaches, and operational risks when critical functions are compromised.
Did you know that 2023 was the worst-ever year for breached healthcare records? According to a report by The HIPAA Journal, breached healthcare records increased by 156% from 2022. On average, about 373,788 healthcare records were breached daily in 2023.
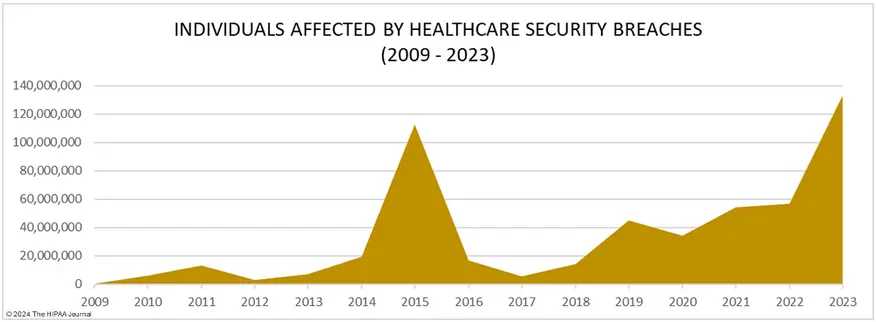
Source: The HIPAA Journal
As technology advances, so do the threats to sensitive medical data. This blog delves into the essential strategies and best practices for enhancing patient data protection through robust healthcare cybersecurity measures.
From encryption protocols, password policies & managers to access controls, and employee training, we explore how healthcare providers must build their defenses against cyber threats. This will help healthcare owners to sustain the trust and confidentiality of patients.
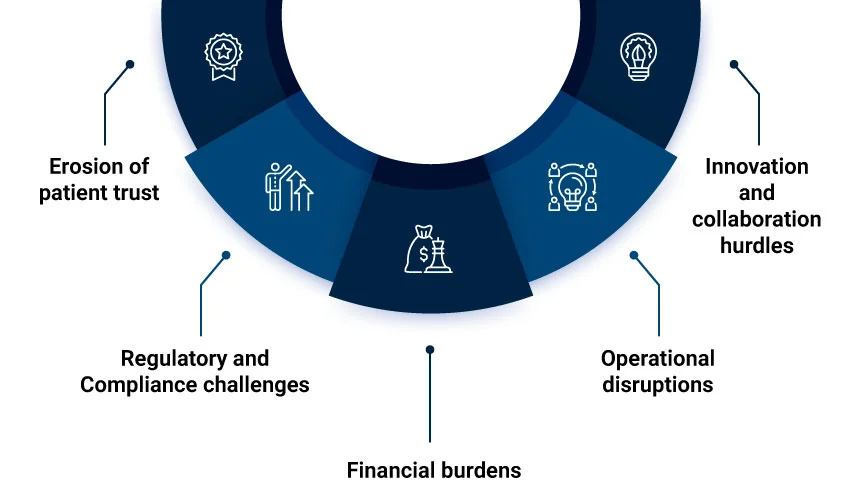
Cyber threats pose a grave risk to healthcare data security, endangering patient privacy, compromising clinical outcomes, and straining financial resources. For example- ransomware attackers can hold medical records or access to lifesaving medical devices as hostage. Such attacks can lead to costly repercussions, compromised patient care, and potential identity theft.
It should be no surprise that an individual’s complete healthcare record can be sold at a very high price. According to Statista’s report, the medical industry faces the highest cost per stolen record at about $429 due to data breaches.
The healthcare industry faces significant cybersecurity threats that can compromise patient data and disrupt operations. The most common threats include:
These attacks can lead to the encryption of sensitive data, hindering access to patient records and potentially risking patient care. As per a recent analysis, about 141 hospitals faced ransomware attacks in 2023.
Phishing emails with malicious links pose a significant threat by tricking users into revealing sensitive information, compromising data security. The HIPAA journal mentions that phishing is an important cause of healthcare data breaches.
Internal staff posing risks through unauthorized access or malicious actions can jeopardize patient privacy and data integrity. Verizon’s 2023 data breach investigations report says miscellaneous errors, misdelivery, and privilege misuse patterns are common in healthcare. All three stem from insiders.
Vulnerabilities in implantable medical devices, such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, and infusion pumps, are constantly exploited. Issues with web interfaces and default hard-coded administration passwords threaten patient safety and data integrity.
Data breaches via unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive patient information stem from system vulnerabilities, inadequate security protocols, or deliberate, targeted attacks, posing substantial risks to patient privacy and identity theft.

Healthcare organizations must proactively adopt strategies to build cybersecurity defenses and defend against cyberattacks and data breaches. Here’s how healthcare CIOs can stay ahead of cyber threats and implement robust security measures:
Utilizing encryption methods like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) helps secure electronic protected health information (ePHI) by converting it into a coded format. This can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key. It ensures data confidentiality and integrity, especially when data is transmitted or stored.
Implementing access control measures involves setting up role-based access controls, biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication, and strict user permissions.
It helps to limit data access to authorized personnel only. This also prevents unauthorized users from viewing or modifying sensitive patient information, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Conducting routine security audits and risk assessments allows healthcare organizations to identify vulnerabilities, assess security posture, and proactively address potential threats.
By regularly evaluating systems, processes, and controls, organizations can detect weaknesses, implement necessary improvements, and stay compliant with industry regulations to ensure ongoing protection of patient data.
By leveraging the latest technological advancements in blockchain, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud, healthcare organizations can ensure confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of patient information:
Blockchain technology ensures data integrity by creating a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger of transactions. In healthcare, blockchain can store patient records securely, ensuring data immutability and transparency.
AI and machine learning are utilized for threat detection in healthcare systems. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential security breaches, enhancing the ability to effectively detect and respond to cyber threats.
By encrypting data, implementing access controls, and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, cloud platforms provide a safe environment for storing and managing patient data.
Implementing a comprehensive security plan is essential for safeguarding patient data in healthcare. Here are the critical components:
Healthcare organizations must develop a cybersecurity strategy tailored to their specific needs, considering the sensitivity of patient data and regulatory requirements like HIPAA. This strategy should include risk assessments, threat intelligence, security controls, and incident response protocols to mitigate cyber threats effectively.
Educating the team on cybersecurity best practices is crucial in preventing data breaches. Training programs should cover phishing awareness, password hygiene, device security, and incident reporting to empower employees to proactively recognize and respond to potential security threats.
Establishing an incident response plan for data breaches is essential for minimizing the impact of security incidents. This plan should outline roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, containment procedures, forensic analysis, recovery strategies, and post-incident reviews to ensure a swift and coordinated response to security breaches.
By implementing these components, healthcare organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and establish a proactive approach to minimize damage and reduce losses.
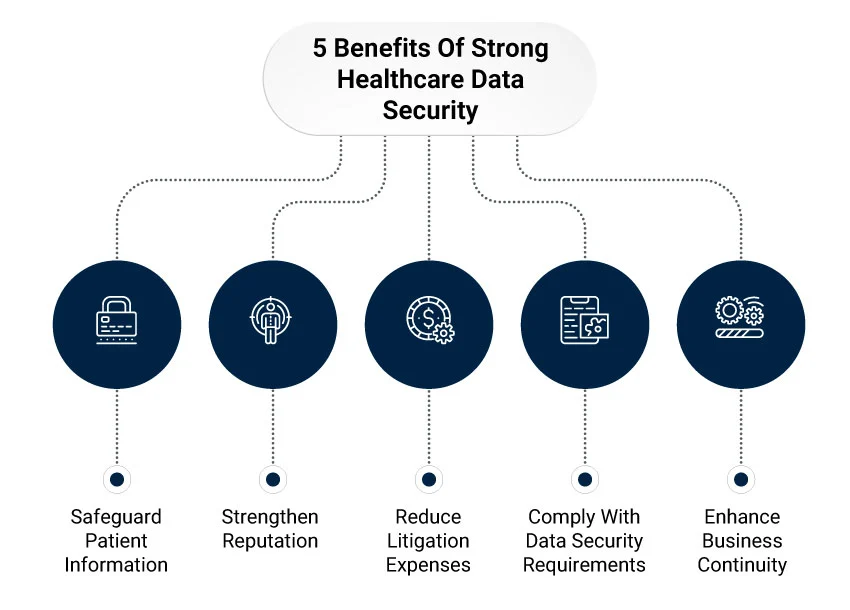
Enhancing patient data protection through robust cybersecurity strategies is critical in safeguarding sensitive information, maintaining trust, and ensuring compliance in the healthcare sector. Implementing encryption techniques, access controls, regular security audits, and leveraging blockchain, AI, and cloud security solutions are great ways to build cyber defenses.
Training staff in cybersecurity best practices and developing incident response plans further strengthens the resilience of healthcare systems in the face of evolving security challenges. Embracing a comprehensive security plan tailored to healthcare needs protects patient data and upholds healthcare services’ integrity. By prioritizing patient data protection and staying vigilant against emerging threats, healthcare providers can maintain their commitment to patient privacy and data security.
The healthcare industry is on the verge of significant transformation, with innovations and external influences bringing new risks. Now more than ever, it is crucial for cybersecurity and privacy to be seamlessly integrated into the implementation of healthcare services.
Industry stakeholders must proactively address the evolving landscape incorporating security measures by design to navigate future challenges responsibly. Embracing these changes not only ensures the advancement of healthcare but also paves the way for a safe and secure future in the healthcare ecosystem.
Learn how Synoptek healthcare IT experts can help you in this journey.
